Welcome!
In this jupyter notebook, as an example, we are going to analyse 10 croped images of a bread sample, having \(Kondis\) with extra gluten, baked by convection heating and imaged in the middle of the bread (series \(Extra-Convection-Middle\)).
5 images at the very beginning of the baking (indexes 1 to 5), and 5 images at the very end of the baking (indexes 6 to 10).
# Import Libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tifffile import imread, imsave
import skimage.measure
import pickle as pkl
import os
import spam
# Import FoamQuant library
from FoamQuant import *
# Set matplotlib default font size
plt.rc('font', size=20)
Part 1: Image processing
# Create the processing pipeline
ProcessPipeline = ['P1_Raw',
'P2_PhaseSegmented',
'P3_Cleaned',
'P4_PoreSegmented',
'P5_PoreNoEdge',
'P6_WallThickness',
'P7_Contact']
for Pi in ProcessPipeline:
if os.path.exists(Pi):
print('path already exist:',Pi)
else:
print('Created:',Pi)
os.mkdir(Pi)
path already exist: P1_Raw
path already exist: P2_PhaseSegmented
path already exist: P3_Cleaned
path already exist: P4_PoreSegmented
path already exist: P5_PoreNoEdge
path already exist: P6_WallThickness
path already exist: P7_Contact
A) The raw images
# Read/Save image names and directories
nameread = 'Raw_'
namesave = 'PhaseSegmented_'
dirread = ProcessPipeline[0]+'/'
dirsave = ProcessPipeline[1]+'/'
# Images indexes:
# -> 1 to 5 are the 5 first images of the series
# -> 6 to 10 are the 5 last images of the series
imrange = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
# Read the first and last image of the series
RawFirst = imread(dirread+nameread+strindex(imrange[0], 3)+'.tif')
RawLast = imread(dirread+nameread+strindex(imrange[-1], 3)+'.tif')
# Show a 3D-cut view of the two volume
Cut3D(RawFirst,
showcuts=True,
showaxes=True,
figblocksize=7,
zcut=50, # tune this parrameter if you wish
ycut=False, # tune this parrameter if you wish
xcut=False, # tune this parrameter if you wish
cmap='bone')
Cut3D(RawLast,
showcuts=True,
showaxes=True,
figblocksize=7,
zcut=50, # tune this parrameter if you wish
ycut=False, # tune this parrameter if you wish
xcut=False, # tune this parrameter if you wish
cmap='bone')
Example of raw images in the beginning of baking
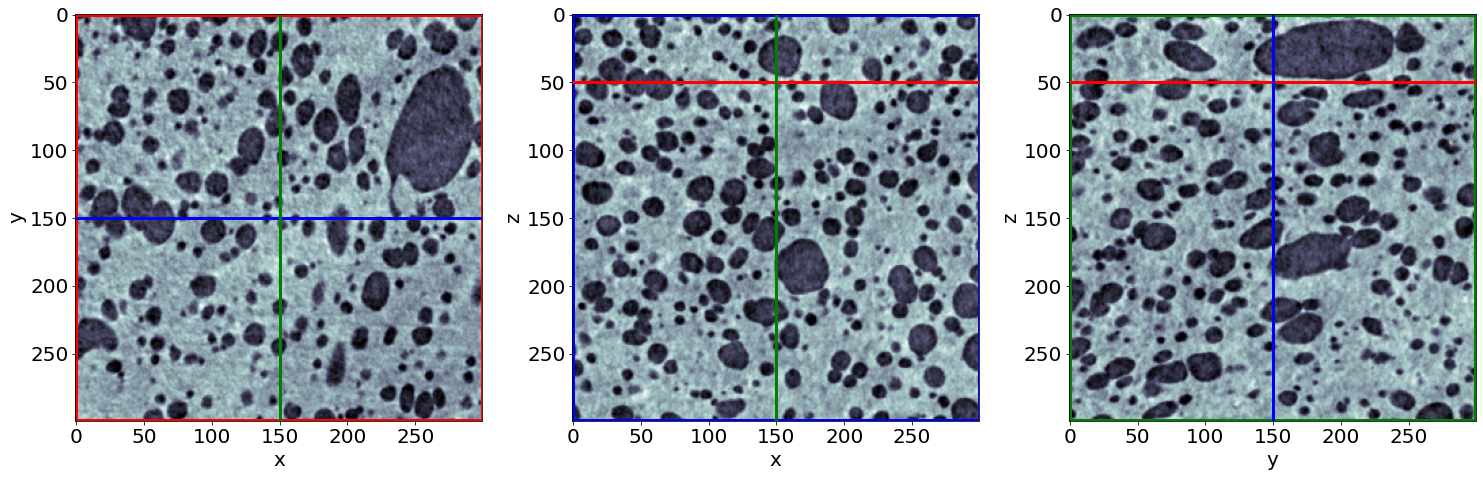
Example of raw images in the end of baking
B) Phase segmentation
# Otsu simple threshold phase segmentation of the whole series
th = PhaseSegmentation_Batch(nameread,
namesave,
dirread,
dirsave,
imrange,
method='ostu_global',
returnOtsu=True,
verbose=True,
n0=3,
endread='.tif',
endsave='.tif')
PhaseSegmented_ 1: done
PhaseSegmented_ 2: done
PhaseSegmented_ 3: done
PhaseSegmented_ 4: done
PhaseSegmented_ 5: done
PhaseSegmented_ 6: done
PhaseSegmented_ 7: done
PhaseSegmented_ 8: done
PhaseSegmented_ 9: done
PhaseSegmented_ 10: done
# Otsu thresholds used for the segmentation
print('Otsu thresholds:',th)
Otsu thresholds: [93, 93, 94, 94, 94, 94, 94, 94, 94, 94]
Let’s see the result…
# Read the first and last image of the series
SegFirst = imread(dirsave+namesave+strindex(imrange[0], 3)+'.tif')
SegLast = imread(dirsave+namesave+strindex(imrange[-1], 3)+'.tif')
# Let's see the result for the first image
zcut=50 # tune this parrameter if you wish
ycut=False # tune this parrameter if you wish
xcut=False # tune this parrameter if you wish
cmap='bone' # tune this parrameter if you wish: e.g. 'bone'
# Show a 3D-cut view of the volume
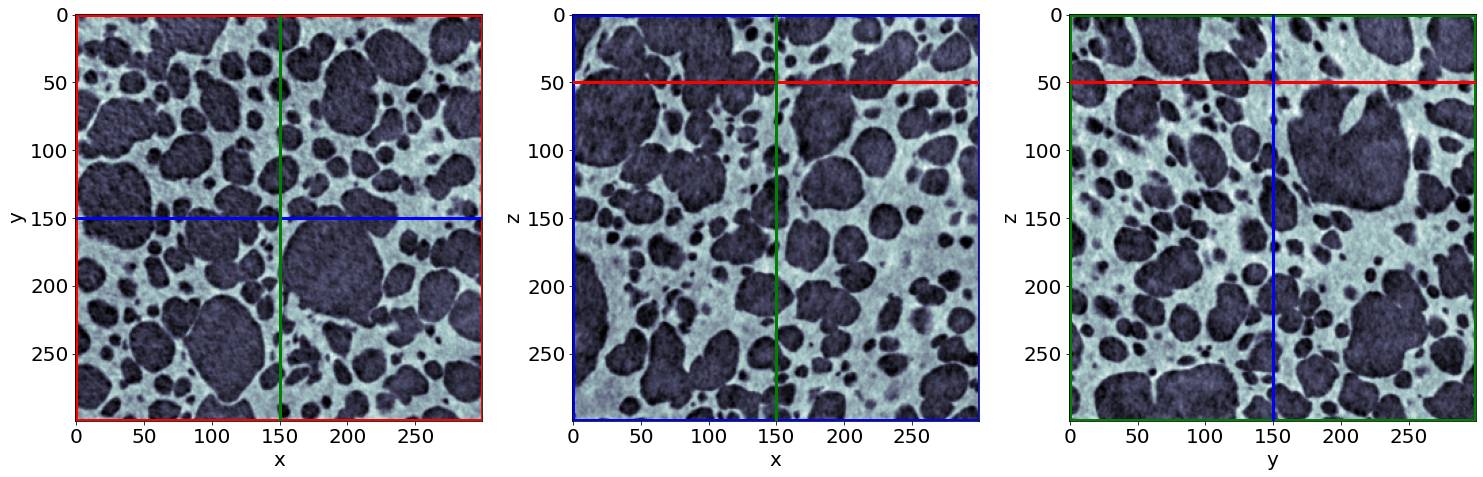
Cut3D(SegFirst, showcuts=True, showaxes=True, figblocksize=7,zcut=zcut,ycut=ycut,xcut=xcut, cmap=cmap) # Phase segmented image
Cut3D((SegFirst>0)*RawFirst, showcuts=True, showaxes=True, figblocksize=7,zcut=zcut,ycut=ycut,xcut=xcut, cmap=cmap) # Phase segmented image * Raw image
Cut3D((1-SegFirst)*RawFirst, showcuts=True, showaxes=True, figblocksize=7,zcut=zcut,ycut=ycut,xcut=xcut, cmap=cmap) # (1-Phase segmented image) * Raw image
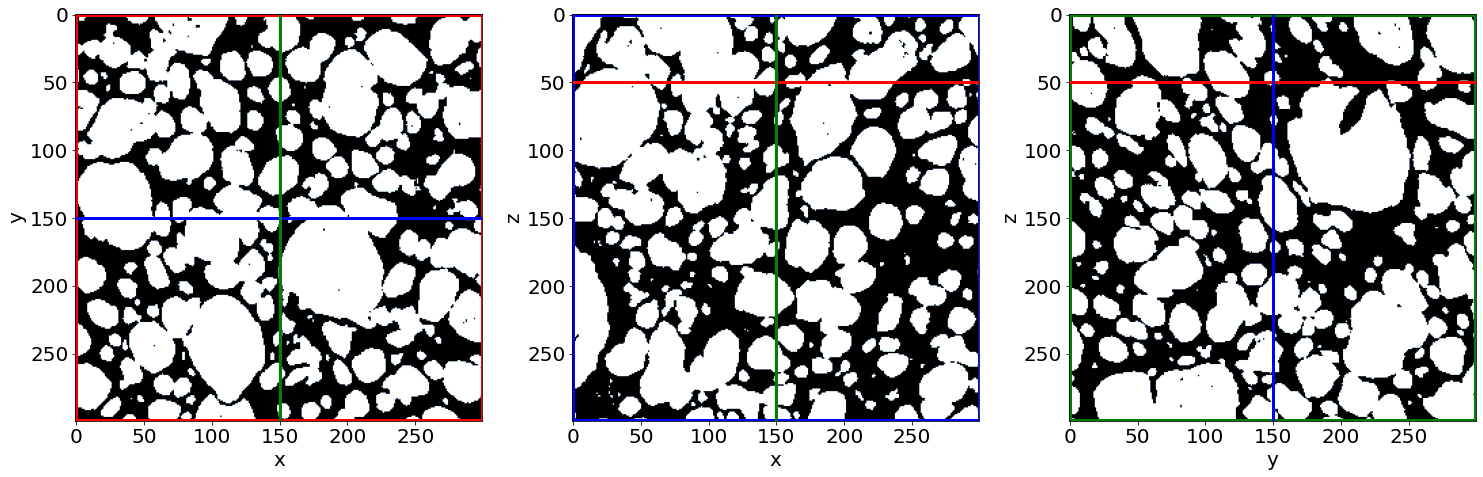
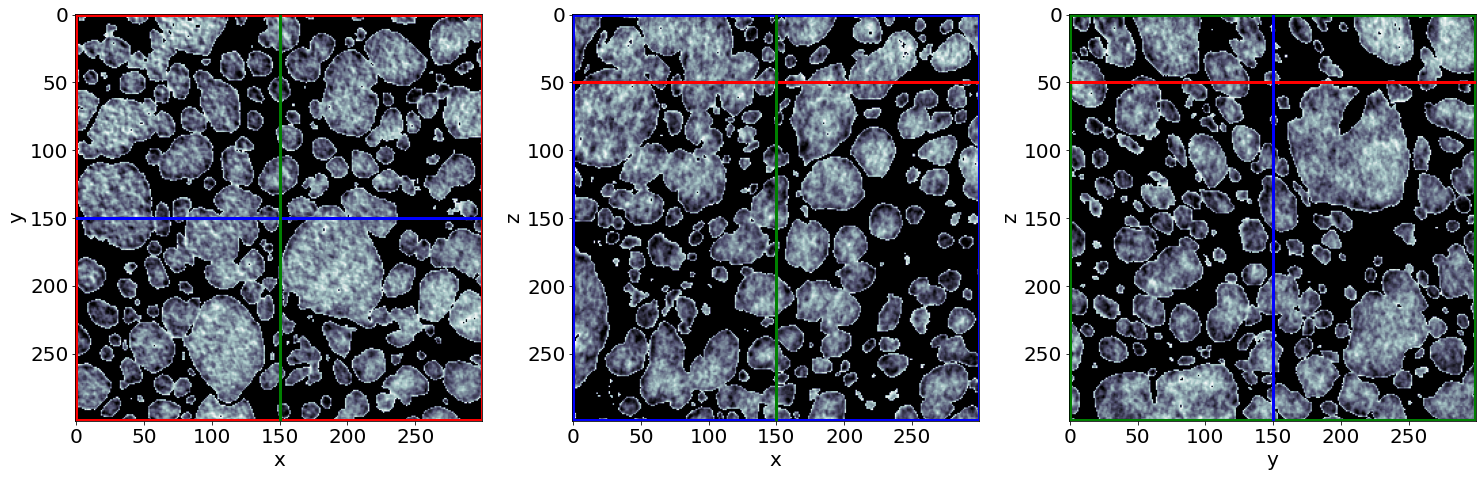
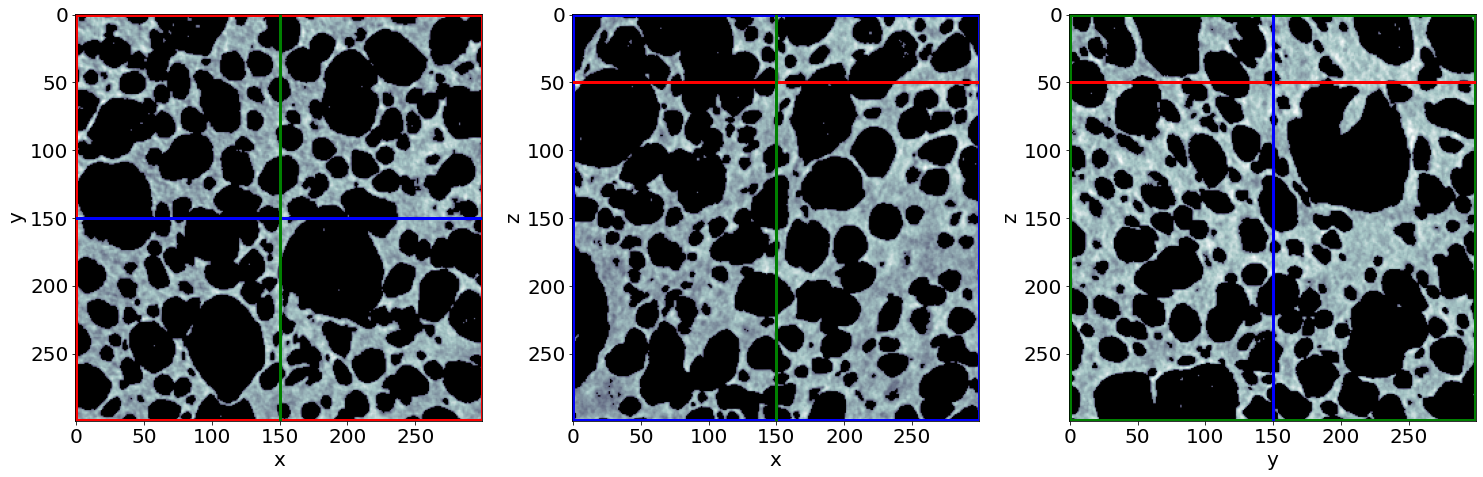
Check the phase segmentation of the first raw image (in the beginning of baking)
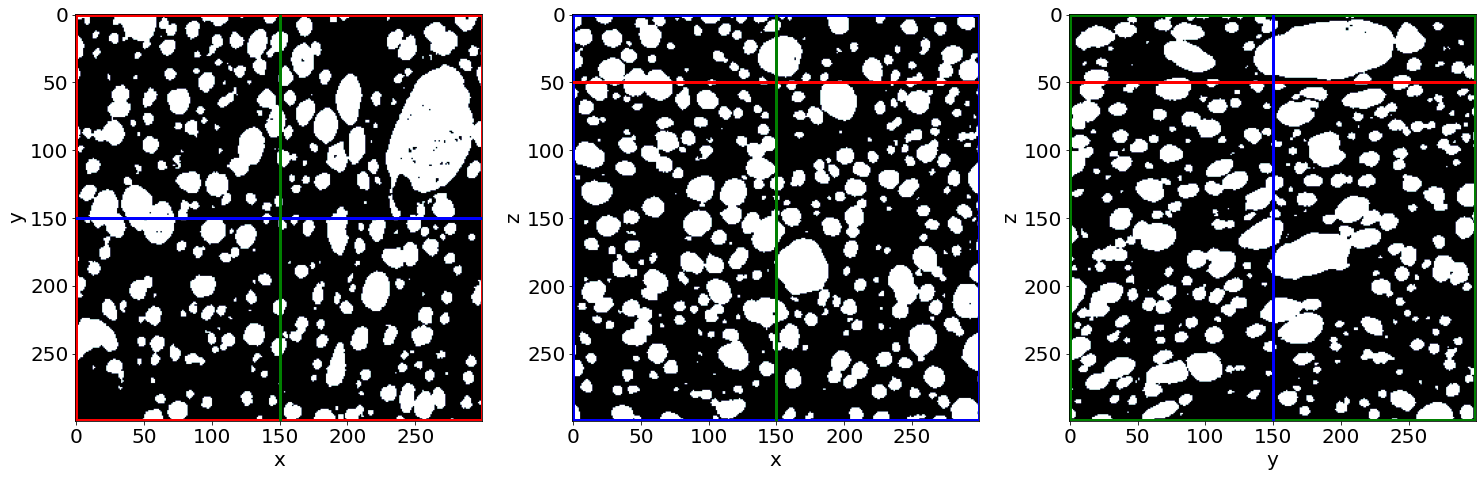
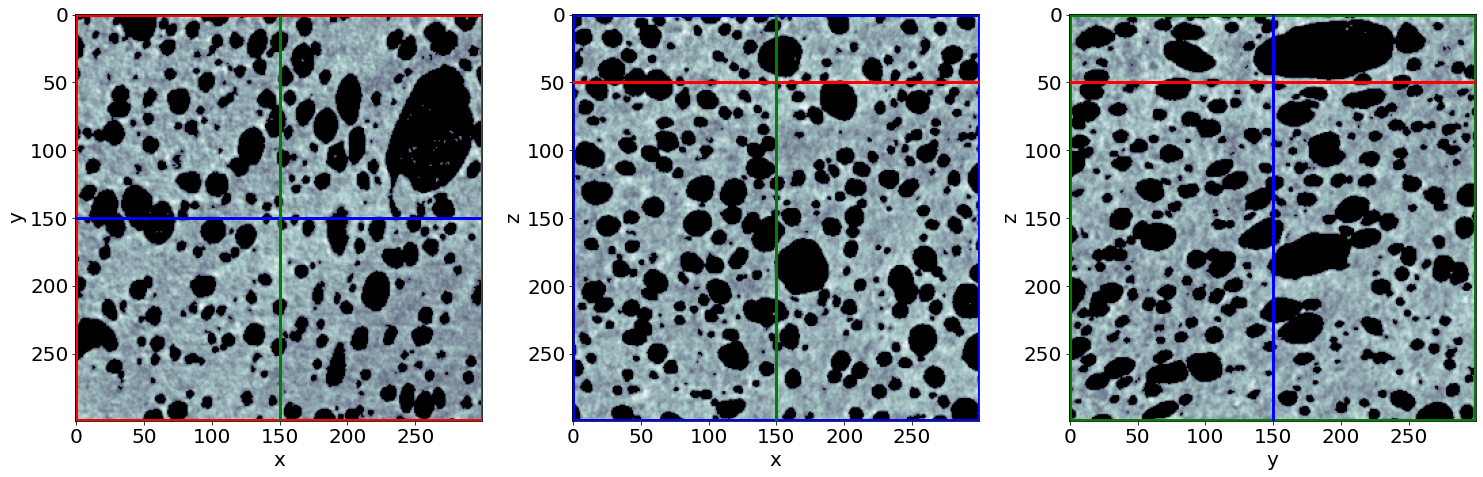
# Let's see the result for the last image
zcut=50 # tune this parrameter if you wish
ycut=False # tune this parrameter if you wish
xcut=False # tune this parrameter if you wish
cmap='bone' # tune this parrameter if you wish: e.g. 'bone'
# Show a 3D-cut view of the volume
Cut3D(SegLast, showcuts=True, showaxes=True, figblocksize=7,zcut=zcut,ycut=ycut,xcut=xcut, cmap=cmap) # Phase segmented image
Cut3D((SegLast>0)*RawLast, showcuts=True, showaxes=True, figblocksize=7,zcut=zcut,ycut=ycut,xcut=xcut, cmap=cmap) # Phase segmented image * Raw image
Cut3D((1-SegLast)*RawLast, showcuts=True, showaxes=True, figblocksize=7,zcut=zcut,ycut=ycut,xcut=xcut, cmap=cmap) # (1-Phase segmented image) * Raw image
Check the phase segmentation of the last raw image (in the end of baking)
C) Remove small holes & regions
Due to artefacts the phase segmented images can have speckles, e.g. small pore regions (1, white) and holes (0, black). In our case (bread images), this is problematic for the pore segmentations. One may oversegment the pores due to small holes flowting in the middle of the pore regions.
Since in the bread images the solid phase consist of a unique region (0, black), one can filter all the small holes.
However for the small pore regions (1, white), we cannot be sure. They may be speckle artefacts or actual pores in the bread. Therefore they are not going to be filtered. All the pore having a volumes below 3x3x3=27 voxels should be disgarded because of the this resolution limitation.
# Read/Save image names and directories
nameread = 'PhaseSegmented_'
namesave = 'Cleaned_'
dirread = ProcessPipeline[1]+'/'
dirsave = ProcessPipeline[2]+'/'
# Images indexes
imrange = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
Remove all holes with: - Vhole < Chole * max(Vhole)
Since in bread images, the solid phase consist of unique large regions, Chole can be strict (large thresholds). All the other smaller regions are often due to imaging artefacts.
# remove holes and objects
RemoveSpeckleBin_Batch(nameread,
namesave,
dirread,
dirsave,
imrange,
verbose=True,
RemoveObjects=False,
RemoveHoles=True,
BinClosing=False,
endread='.tif',
endsave='.tif',
n0=3,
Chole=0.1) # tune this parrameter if you wish
Before: Nobj 6104
After: Nobj 1
Before: Nhol 983
After: Nhol 1
First image (vox): maxObj 4987372 maxHole 22006312
Thresholds (vox): thrObj 2493686 thrHole 2200631
Before: Nhol 1316
After: Nhol 1
Cleaned_001: done
Before: Nhol 1283
After: Nhol 1
Cleaned_002: done
Before: Nhol 1212
After: Nhol 1
Cleaned_003: done
Before: Nhol 1384
After: Nhol 1
Cleaned_004: done
Before: Nhol 1418
After: Nhol 1
Cleaned_005: done
Before: Nhol 1868
After: Nhol 1
Cleaned_006: done
Before: Nhol 1945
After: Nhol 1
Cleaned_007: done
Before: Nhol 1878
After: Nhol 1
Cleaned_008: done
Before: Nhol 1928
After: Nhol 1
Cleaned_009: done
Before: Nhol 2064
After: Nhol 1
Cleaned_010: done
# Read the first image of the series
Seg = imread(dirread+nameread+strindex(imrange[0], 3)+'.tif')
Cleaned = imread(dirsave+namesave+strindex(imrange[0], 3)+'.tif')
zcut=50 # tune this parrameter if you wish
ycut=False # tune this parrameter if you wish
xcut=False # tune this parrameter if you wish
cmap='bone' # tune this parrameter if you wish: e.g. 'bone'
# Show a 3D-cut view of the volume
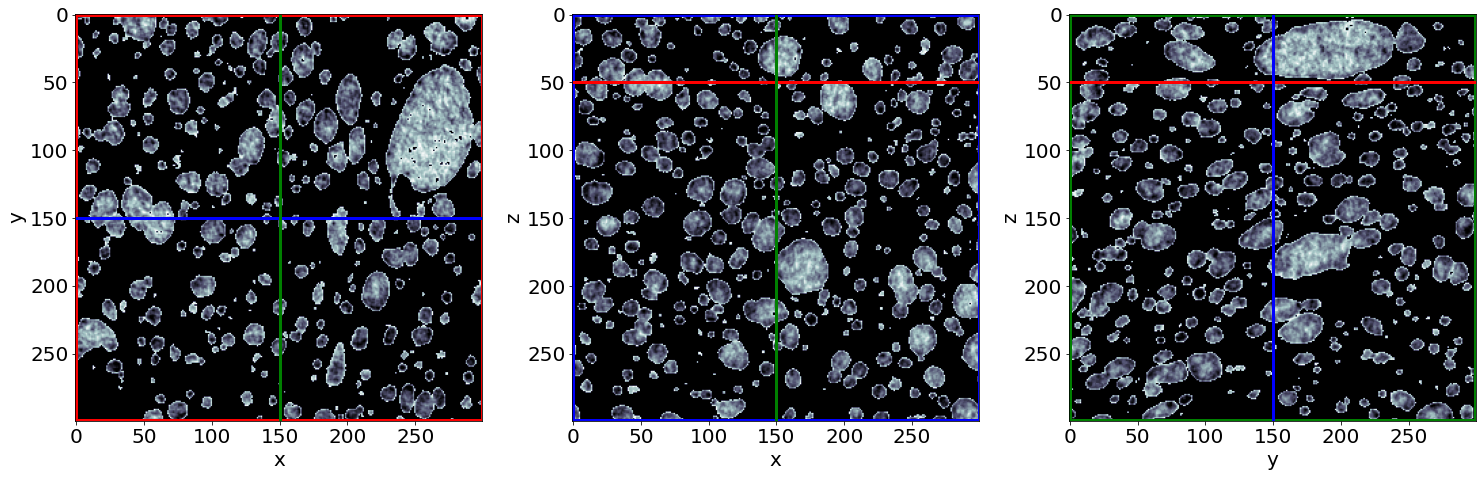
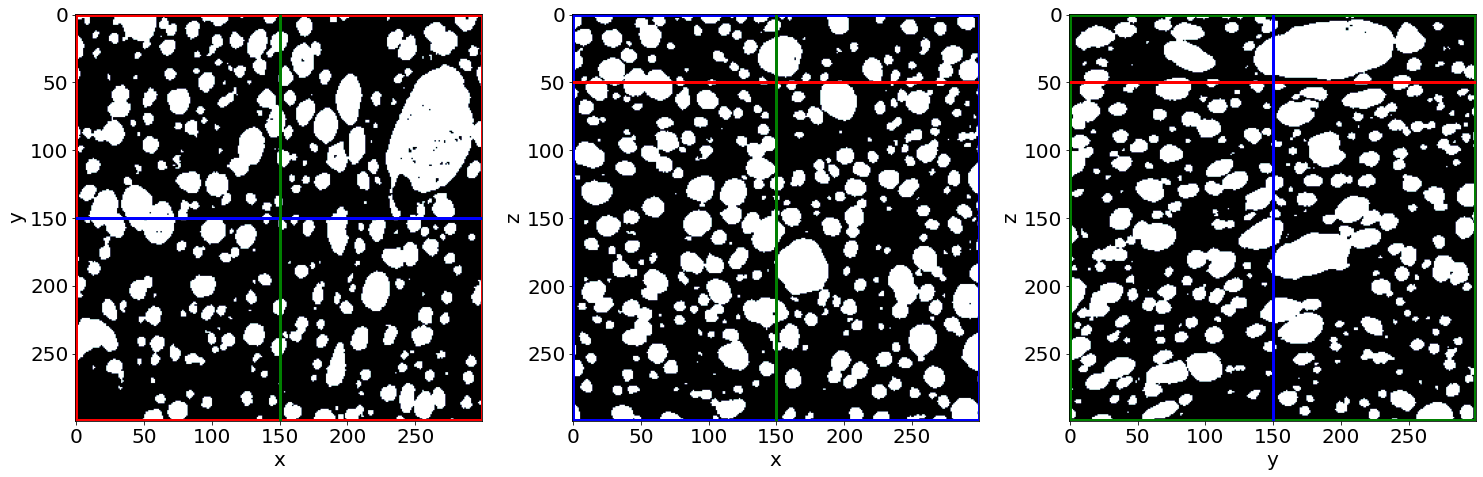
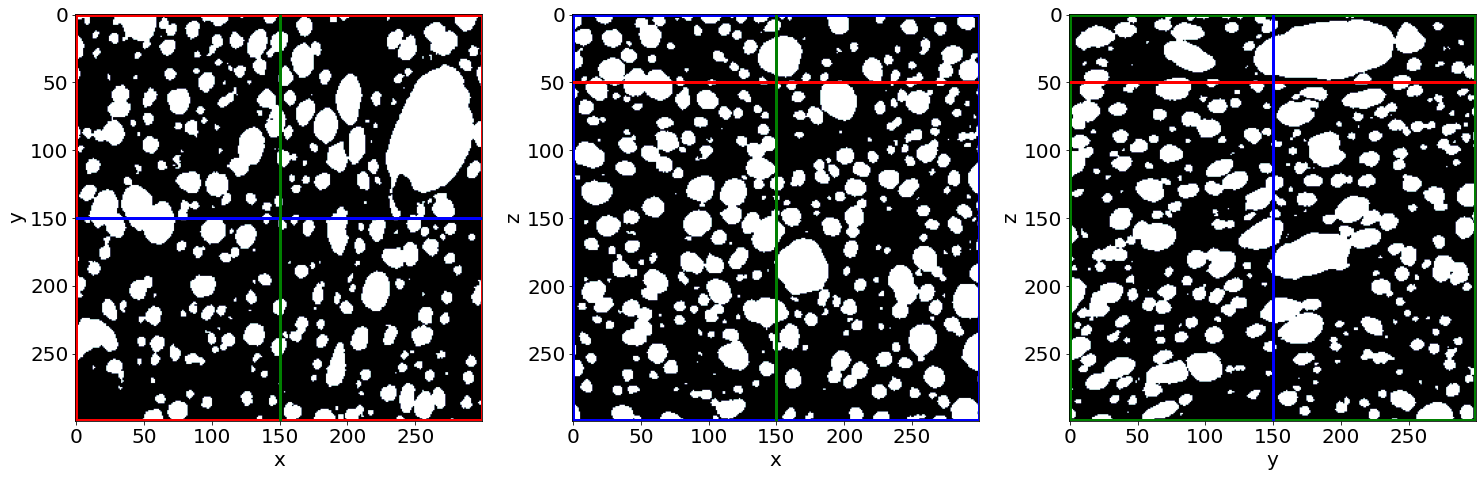
Cut3D(Seg, showcuts=True, showaxes=True, figblocksize=7,zcut=zcut,ycut=ycut,xcut=xcut, cmap=cmap)
Cut3D(Cleaned, showcuts=True, showaxes=True, figblocksize=7,zcut=zcut,ycut=ycut,xcut=xcut, cmap=cmap)
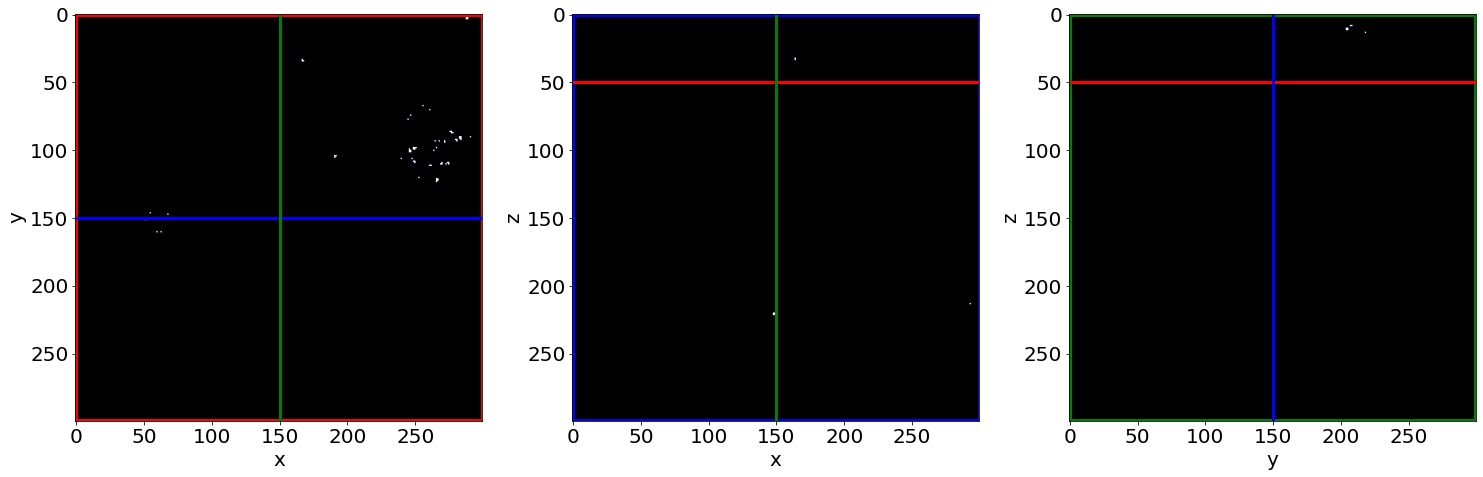
Cut3D(Cleaned-Seg, showcuts=True, showaxes=True, figblocksize=7,zcut=zcut,ycut=ycut,xcut=xcut, cmap=cmap)
Check the small holes removal in the first image of the series (in the beginning of baking)
D) Labelled images
# Read/Save image names and directories
nameread = 'Cleaned_'
namesave = 'PoreSeg_'
dirread = ProcessPipeline[2]+'/'
dirsave = ProcessPipeline[3]+'/'
# Images indexes
imrange = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
# Segment the pores with ITK watershed (ITK=True) implemented in SPAM (works well for polydispersed and elongated pores)
# if you wish, you can also try the default watershed segmentation, and play with the segmentation parrameters (ITK=False)
BubbleSegmentation_Batch(nameread,
namesave,
dirread,
dirsave,
imrange,
ITK=True,
ITKLevel=1,
verbose=True,
endread='.tif',
endsave='.tif',
n0=3)
Path exist: True
PoreSeg_001: done
PoreSeg_002: done
PoreSeg_003: done
PoreSeg_004: done
PoreSeg_005: done
PoreSeg_006: done
PoreSeg_007: done
PoreSeg_008: done
PoreSeg_009: done
PoreSeg_010: done
# Create a random colormap to distinguish the pores
rcmap = RandomCmap(5000)
Number of labels: 5000

Let’s see the result…
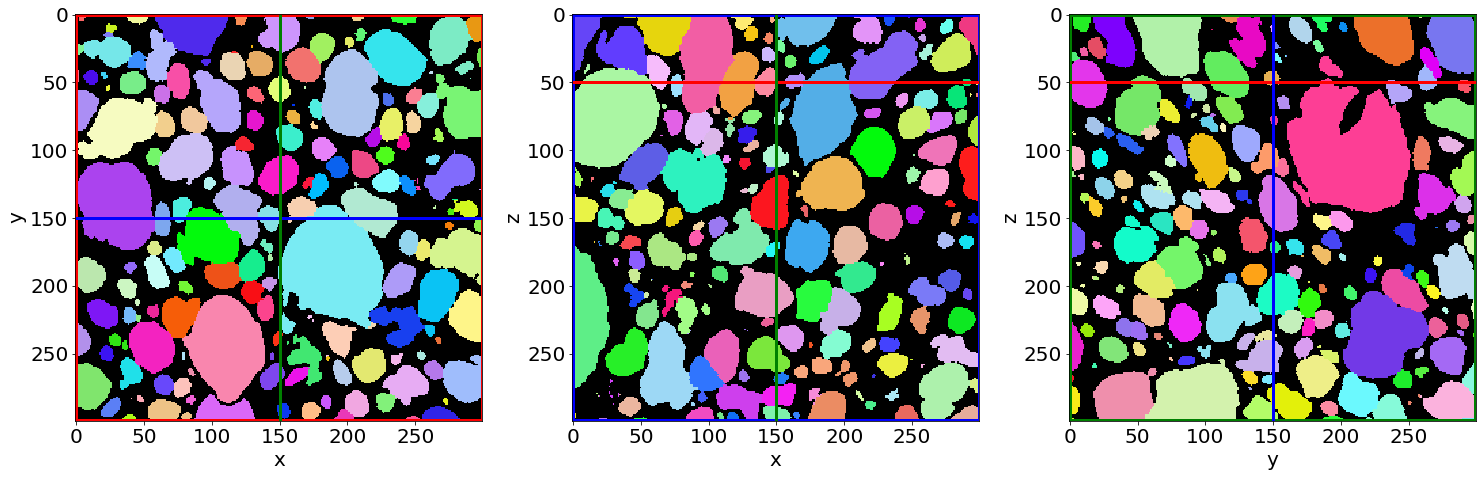
# Read the first image of the series
LabFirst = imread(dirsave+namesave+strindex(imrange[0], 3)+'.tif')
LabLast = imread(dirsave+namesave+strindex(imrange[-1], 3)+'.tif')
# Show a 3D-cut view of the volume
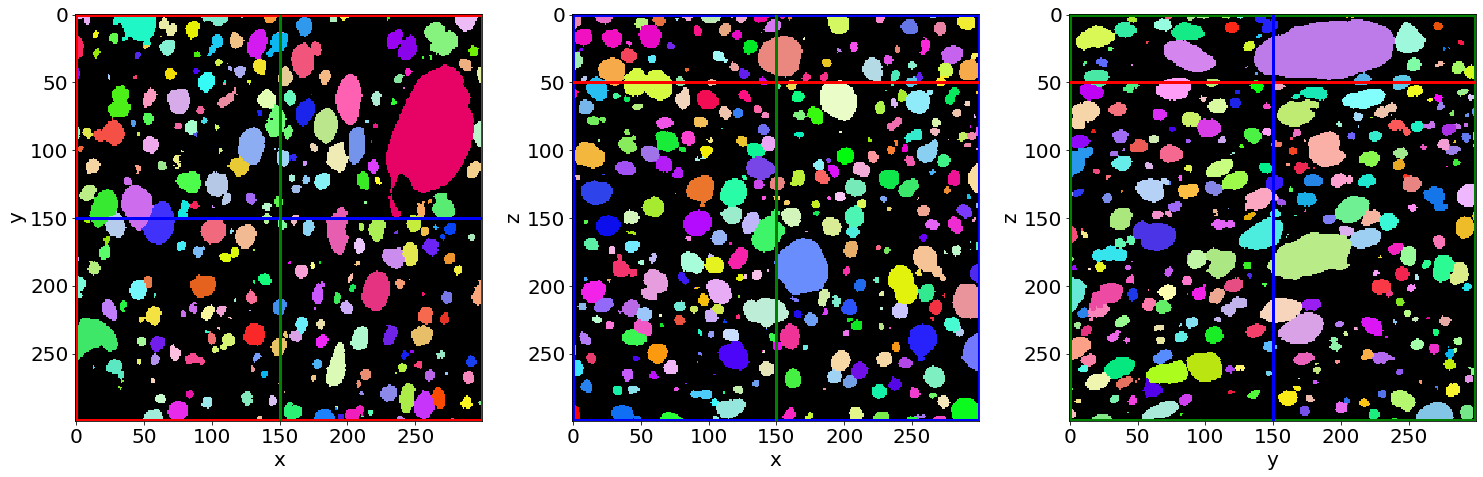
Cut3D(LabFirst,
showcuts=True,
showaxes=True,
cmap=rcmap,
interpolation='nearest',
figblocksize=7, # tune this parrameter if you wish
zcut=50, # tune this parrameter if you wish
ycut=False, # tune this parrameter if you wish
xcut=False) # tune this parrameter if you wish
Cut3D(LabLast,
showcuts=True,
showaxes=True,
cmap=rcmap,
interpolation='nearest',
figblocksize=7, # tune this parrameter if you wish
zcut=50, # tune this parrameter if you wish
ycut=False, # tune this parrameter if you wish
xcut=False) # tune this parrameter if you wish
Check the pores segmentation in the first image of the series (in the beginning of baking)
Check the pores segmentation in the last image of the series (in the end of baking)
-> To visualize the segmentation result in Paraview
Download your ‘random_cmap.json’ and vizualize your pore-segmented image in Paraview
# Create a .json random colormap that can be used in ParaView
json_rand_dictionary(Ncolors=5000, namecmap='random_cmap.json', dirsave = dirsave, first_color_black=True)
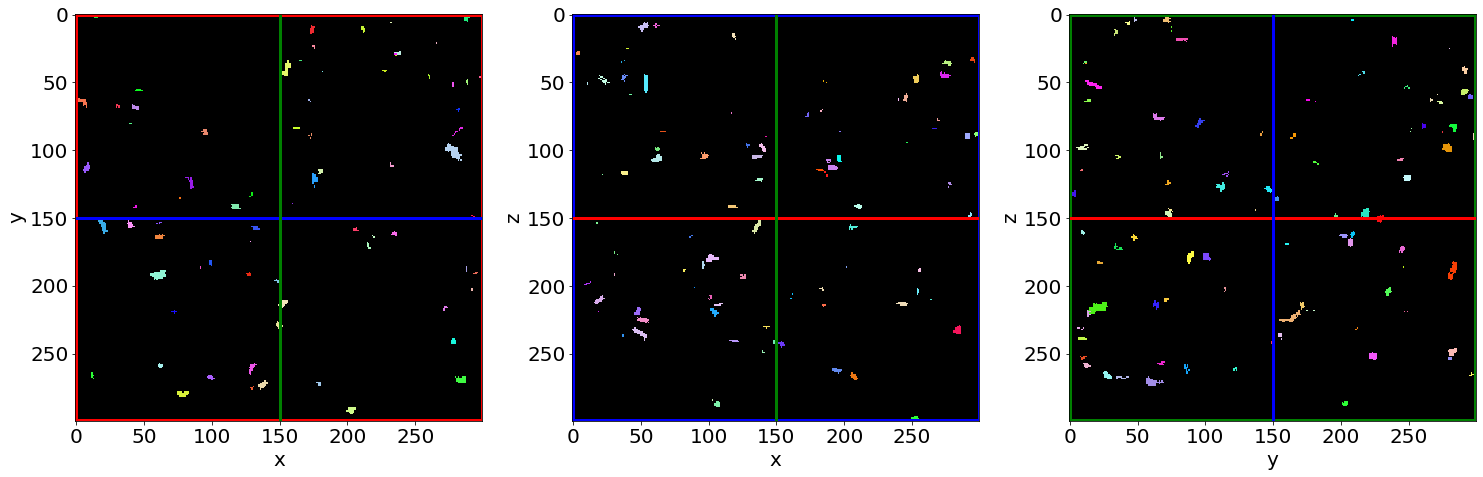
E) Remove the pores at the edges of the image
The pores on the edge of the images (or cut by the mask) are irrelevant for measuring the individual pore properties. To obtain clean statistics, all the pores touching the edges of the image are removed.
# Read/Save image names and directories
nameread = 'PoreSeg_'
namesave = 'PoreNoEdge_'
dirread = ProcessPipeline[3]+'/'
dirsave = ProcessPipeline[4]+'/'
# Images indexes
imrange = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
# Remove the pores at the end of the image (default)
# for more parrameters, try help(BubbleSegmentation_Batch)
RemoveEdgeBubble_Batch(nameread,
namesave,
dirread,
dirsave,
imrange,
verbose=True,
endread='.tif',
endsave='.tif',
n0=3)
Path exist: True
PoreNoEdge_001: done
PoreNoEdge_002: done
PoreNoEdge_003: done
PoreNoEdge_004: done
PoreNoEdge_005: done
PoreNoEdge_006: done
PoreNoEdge_007: done
PoreNoEdge_008: done
PoreNoEdge_009: done
PoreNoEdge_010: done
Let’s see the result…
# Read the first image of the series
NoedgeFirst = imread(dirsave+namesave+strindex(imrange[0], 3)+'.tif')
NoedgeLast = imread(dirsave+namesave+strindex(imrange[-1], 3)+'.tif')
# Show a 3D-cut view of the volume
Cut3D(NoedgeFirst,
showcuts=True,
showaxes=True,
cmap=rcmap,
interpolation='nearest',
figblocksize=7, # tune this parrameter if you wish
zcut=50, # tune this parrameter if you wish
ycut=False, # tune this parrameter if you wish
xcut=False) # tune this parrameter if you wish
Cut3D(NoedgeLast,
showcuts=True,
showaxes=True,
cmap=rcmap,
interpolation='nearest',
figblocksize=7, # tune this parrameter if you wish
zcut=50, # tune this parrameter if you wish
ycut=False, # tune this parrameter if you wish
xcut=False) # tune this parrameter if you wish
Check the pores removal on the edges in the first image of the series (in the beginning of baking)
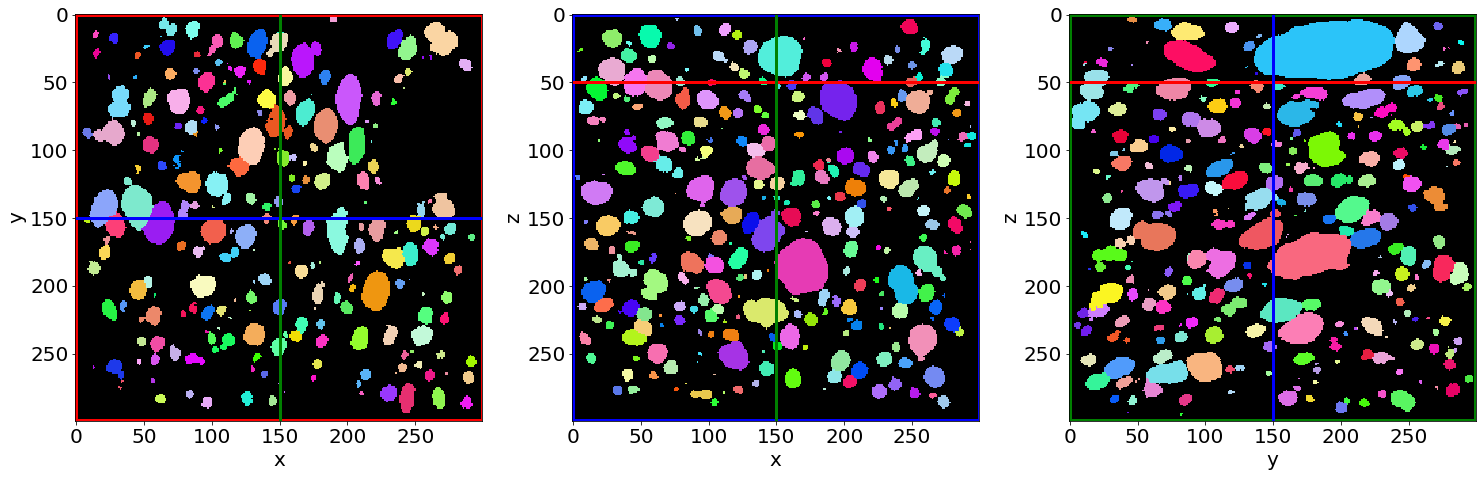
Check the pores removal on the edges in the last image of the series (in the end of baking)
G) Contact images
We can then extract contacts data from the pore-segmented images (both with edges and no-edges are required). The GetContacts function save the coordination table, coordination images and contact table, batchwise.
# Read/Save image names and directories
nameread = 'PoreSeg_'
nameread_noedge = 'PoreNoEdge_'
namesave = 'Contact_'
dirread = ProcessPipeline[3]+'/'
dirread_noedge = ProcessPipeline[4]+'/'
dirsave = ProcessPipeline[6]+'/'
# Images indexes
imrange = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
GetContacts_Batch(nameread, nameread_noedge, namesave, dirread, dirread_noedge, dirsave, imrange,
verbose=False,
endread='.tif',
endread_noedge='.tif',
endsave='.tif',
n0=3,
save='all',
maximumCoordinationNumber=20)
Path exist: True
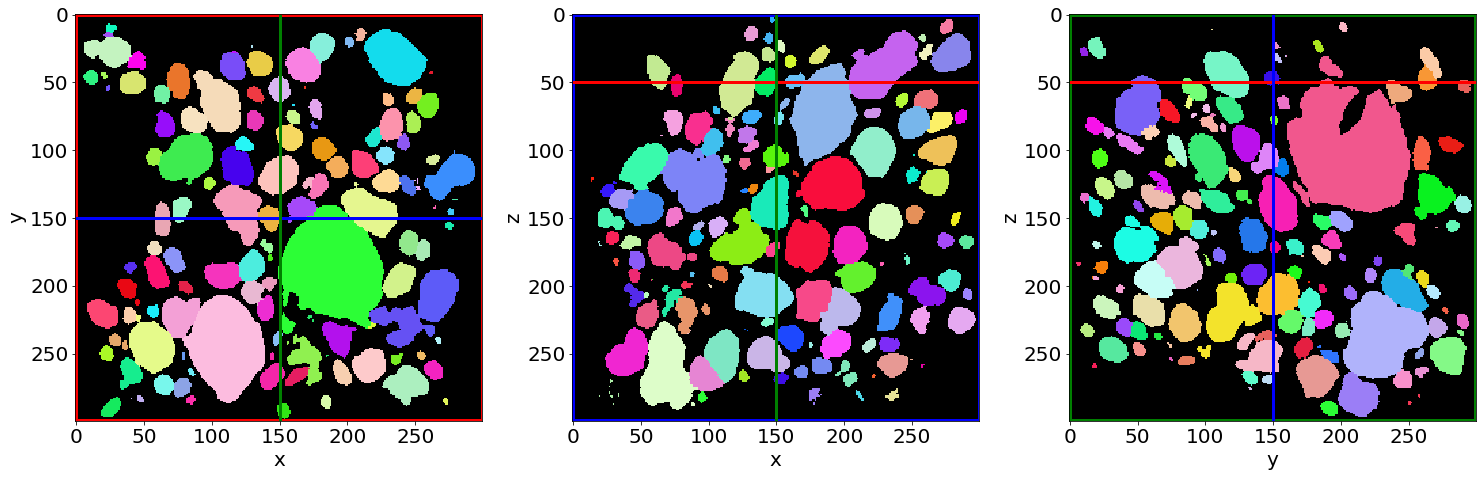
# Read the first image of the series
Lab = imread(dirsave+namesave+strindex(imrange[0], 3)+'.tif')
# Show a 3D-cut view of the volume
Cut3D(Lab,
showcuts=True,
showaxes=True,
cmap=rcmap,
interpolation='nearest',
figblocksize=7, # tune this parrameter if you wish
zcut=False, # tune this parrameter if you wish
ycut=False, # tune this parrameter if you wish
xcut=False) # tune this parrameter if you wish
# Read the last image of the series
Lab = imread(dirsave+namesave+strindex(imrange[-1], 3)+'.tif')
# Show a 3D-cut view of the volume
Cut3D(Lab,
showcuts=True,
showaxes=True,
cmap=rcmap,
interpolation='nearest',
figblocksize=7, # tune this parrameter if you wish
zcut=False, # tune this parrameter if you wish
ycut=False, # tune this parrameter if you wish
xcut=False) # tune this parrameter if you wish
Check the contacts labelling in the first image of the series (in the beginning of baking)
Check the contacts labelling in the last image of the series (in the end of baking)
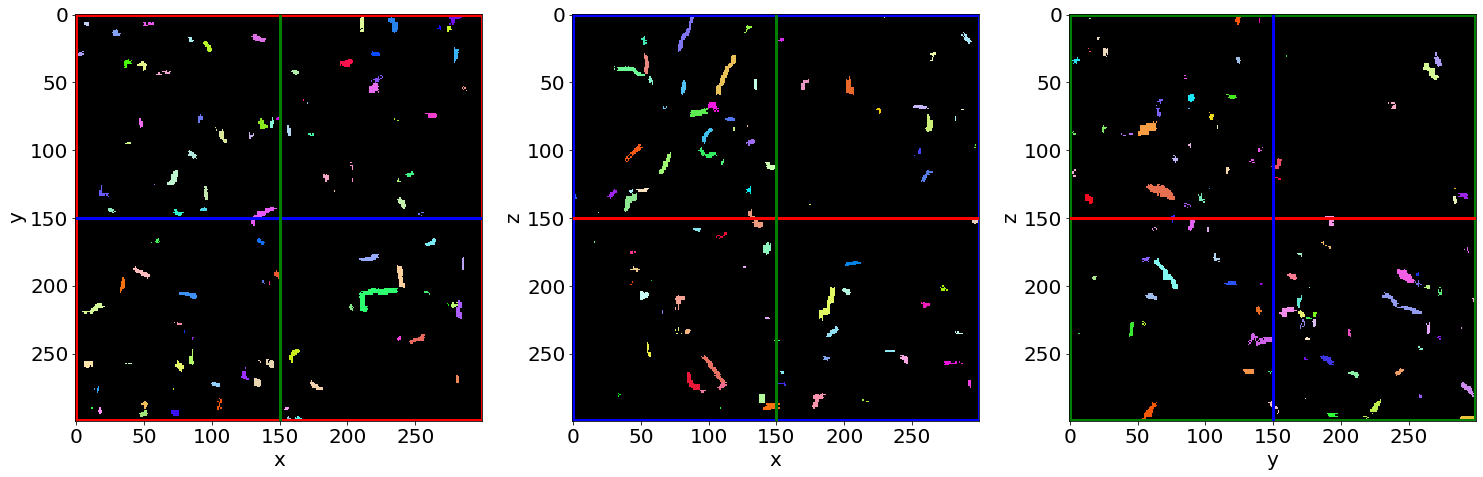
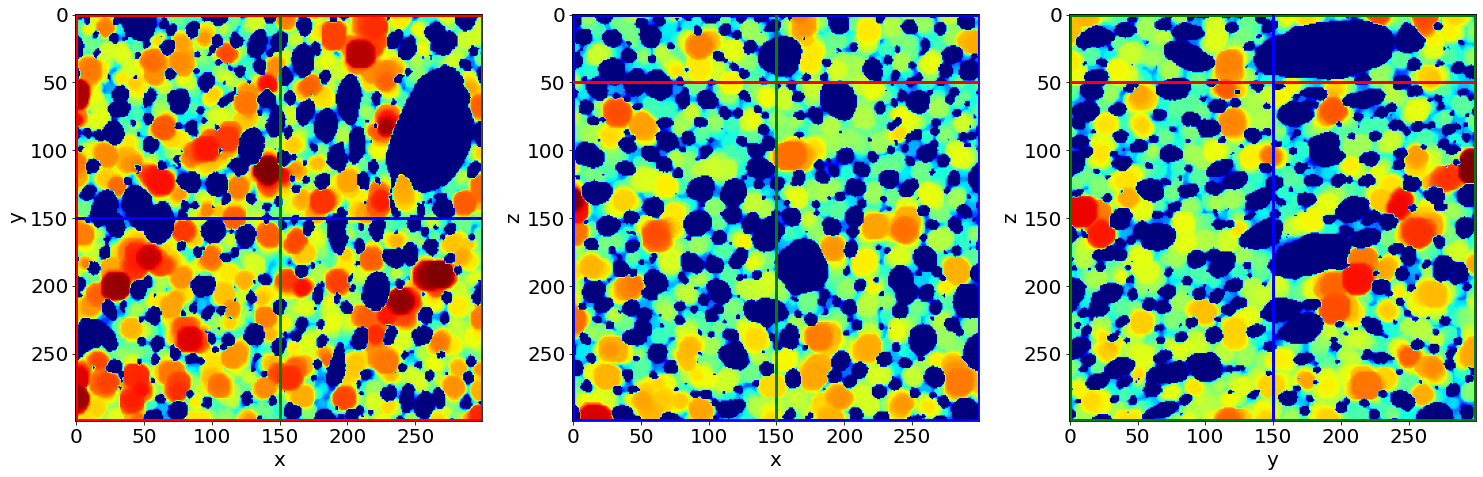
F) Fast Local-wall thickness
Finally, the fast local wall thickness tool developped by Dahl, V. A. and Dahl A. B. (Git-link February 2023: https://github.com/vedranaa/local-thickness.git) can be used to determine the distribution of thicknesses and mean wall thicknes over the whole image.
# If you wish to import the pakage please do as follow
import localthickness as lt
# Read/Save image names and directories
nameread = 'Cleaned_'
namesave = 'WallThickness_'
dirread = ProcessPipeline[2]+'/'
dirsave = ProcessPipeline[5]+'/'
# Images indexes
imrange = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
# The localthickness function is used in FastLocalThickness_Batch for batchwise analysis!
FastLocalThickness_Batch(nameread, namesave, dirread, dirsave, imrange,
verbose=True,
endread='.tif',
endsave='.tif',
n0=3,
WalThickness=True,
Separation=True,
scale=1)
Path exist: True
WallThickness_001: done
WallThickness_002: done
WallThickness_003: done
WallThickness_004: done
WallThickness_005: done
WallThickness_006: done
WallThickness_007: done
WallThickness_008: done
WallThickness_009: done
WallThickness_010: done
Let’s see the result…
# Read the first and last Local Wall thickness images of the series
WTFirst = imread(dirsave+namesave+strindex(imrange[0], 3)+'_WT.tif')
WTLast = imread(dirsave+namesave+strindex(imrange[-1], 3)+'_WT.tif')
# Show a 3D-cut view of the volume
Cut3D(WTFirst,
showcuts=True,
showaxes=True,
cmap='jet',
figblocksize=7, # tune this parrameter if you wish
zcut=50, # tune this parrameter if you wish
ycut=False, # tune this parrameter if you wish
xcut=False) # tune this parrameter if you wish
Cut3D(WTLast,
showcuts=True,
showaxes=True,
cmap='jet',
figblocksize=7, # tune this parrameter if you wish
zcut=50, # tune this parrameter if you wish
ycut=False, # tune this parrameter if you wish
xcut=False) # tune this parrameter if you wish
Check the first local-wall thickness image of the series (in the beginning of baking)
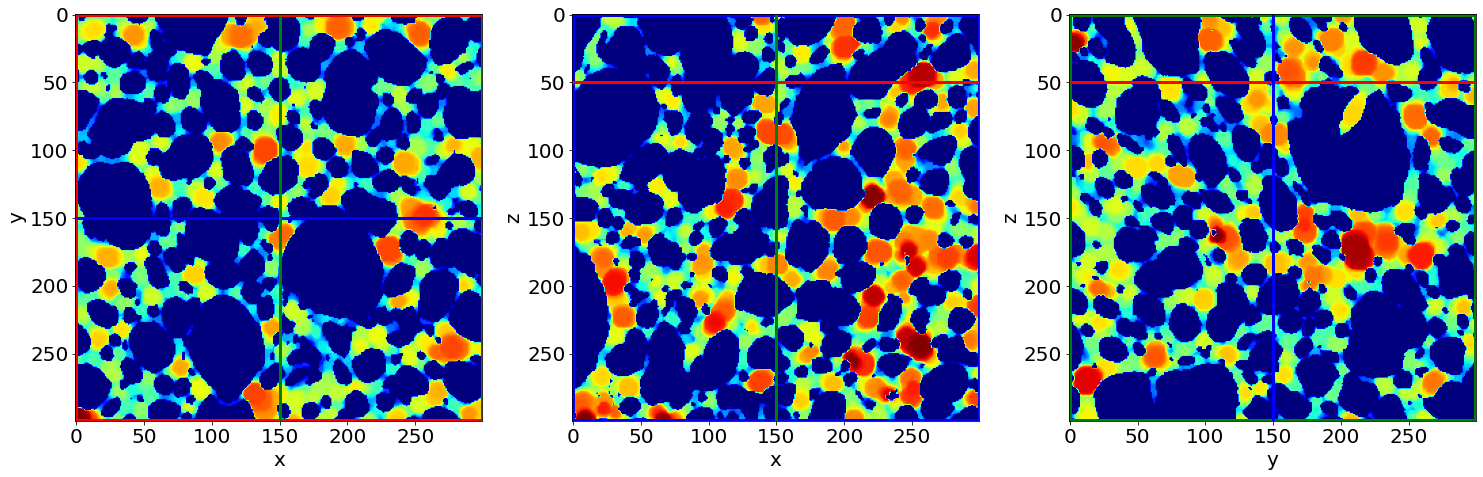
# Read the first and last Separation images of the series
SEPFirst = imread(dirsave+namesave+strindex(imrange[0], 3)+'_SEP.tif')
SEPLast = imread(dirsave+namesave+strindex(imrange[-1], 3)+'_SEP.tif')
# Show a 3D-cut view of the volume
Cut3D(SEPFirst,
showcuts=True,
showaxes=True,
cmap='jet',
figblocksize=7, # tune this parrameter if you wish
zcut=50, # tune this parrameter if you wish
ycut=False, # tune this parrameter if you wish
xcut=False) # tune this parrameter if you wish
Cut3D(SEPLast,
showcuts=True,
showaxes=True,
cmap='jet',
figblocksize=7, # tune this parrameter if you wish
zcut=50, # tune this parrameter if you wish
ycut=False, # tune this parrameter if you wish
xcut=False) # tune this parrameter if you wish
Check the first separation image of the series (in the beginning of baking)
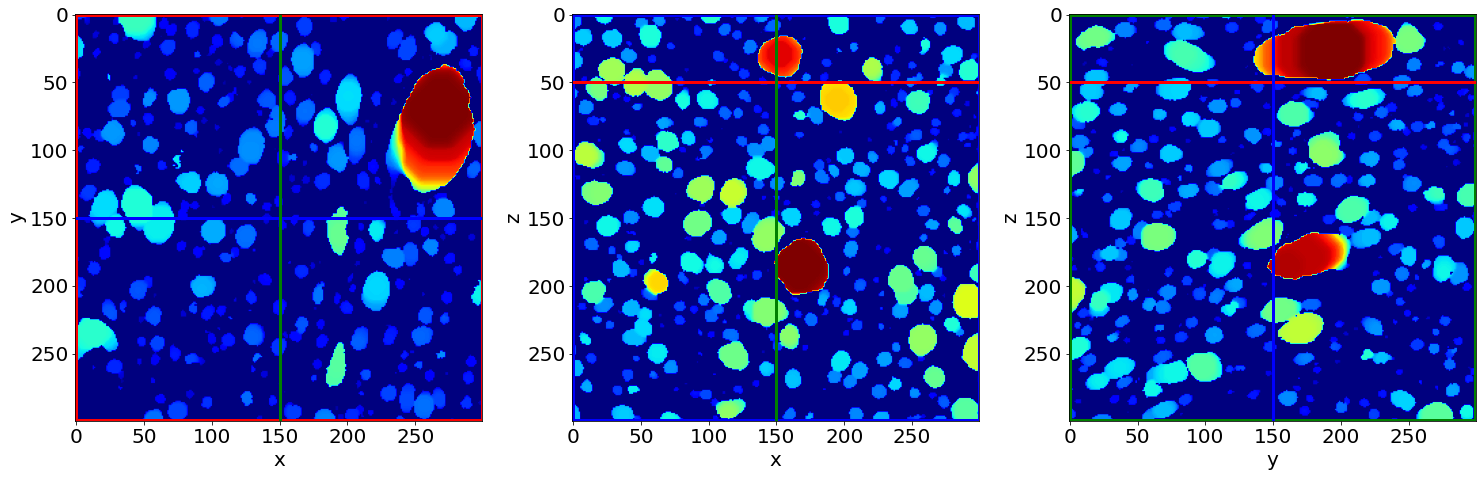
Check the last separation image of the series (in the end of baking)
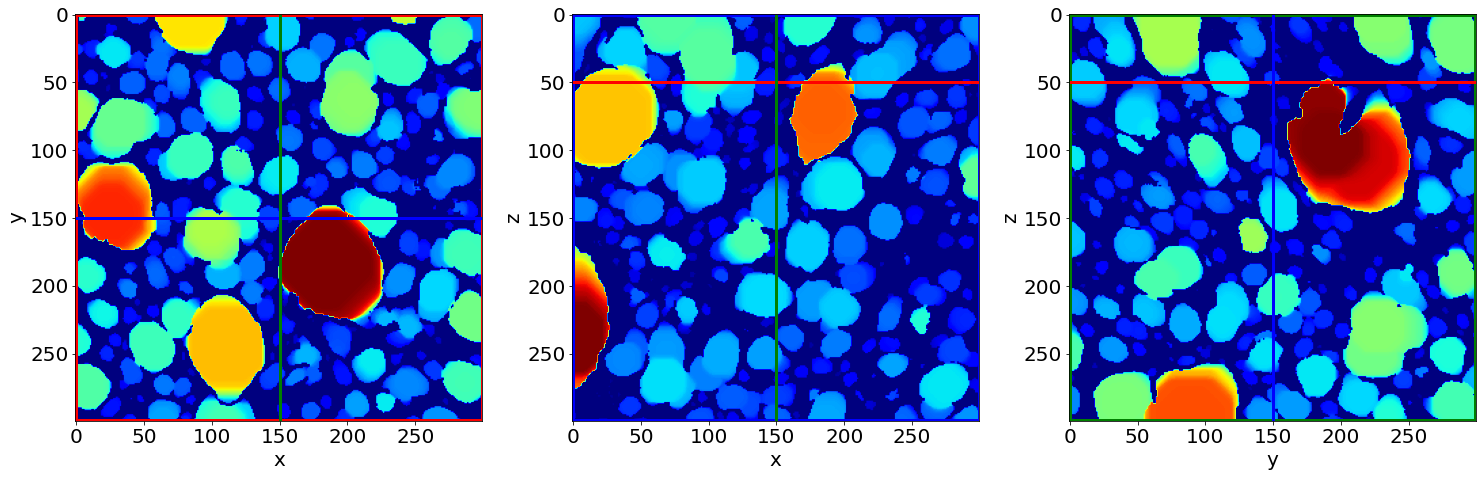
Part 2: Quantification
In this second part, we are going to reuse the processed images for quantifying bread properties:
Porosity \(\phi\)
Volume \(V\), Shape eigenvalues (\(S_1\),\(S_2\),\(S_3\)), Elongation \(E\)
Coordination \(Z\)
Local Wall Thickness \(h_w\)
# Create the quantification folders
QuantFolders = ['Q1_Porosity','Q2_RegProps','Q3_WallThickness']
for Qi in QuantFolders:
if os.path.exists(Qi):
print('path already exist:',Qi)
else:
print('Created:',Qi)
os.mkdir(Qi)
path already exist: Q1_Porosity
path already exist: Q2_RegProps
path already exist: Q3_WallThickness
A) Porosity \(\phi\)
# Read/Save names and directories
nameread = 'Cleaned_'
namesave = 'Porosity_'
dirread = ProcessPipeline[2]+'/'
dirsave = QuantFolders[0]+'/'
# Images indexes
imrange = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
# Get the whole images liquid fraction
# (volume percentage of liquid)
LiqFrac_Batch(nameread,
namesave,
dirread,
dirsave,
imrange,
TypeGrid='Global',
verbose=1,
structured=False)
Path exist: True
Porosity_001: done
Porosity_002: done
Porosity_003: done
Porosity_004: done
Porosity_005: done
Porosity_006: done
Porosity_007: done
Porosity_008: done
Porosity_009: done
Porosity_010: done
## Let's see the result...
# Read the liquid fraction of the first image of the series
LPorosity=[]
for imi in imrange:
with open(dirsave+namesave+strindex(imi,3)+'.pkl','rb') as f:
SF = pkl.load(f)['lf']
print(imi, 'Whole image porosity:',round(1-SF,3),'%')
LPorosity.append(1-SF)
1 Whole image porosity: 0.322 %
2 Whole image porosity: 0.321 %
3 Whole image porosity: 0.323 %
4 Whole image porosity: 0.321 %
5 Whole image porosity: 0.321 %
6 Whole image porosity: 0.578 %
7 Whole image porosity: 0.581 %
8 Whole image porosity: 0.583 %
9 Whole image porosity: 0.585 %
10 Whole image porosity: 0.587 %
# Read/Save names and directories
nameread = 'Cleaned_'
namesave = 'CartesPorosity_'
dirread = ProcessPipeline[2]+'/'
dirsave = QuantFolders[0]+'/'
# Images indexes
imrange = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
# structured = False
LiqFrac_Batch(nameread,
namesave,
dirread,
dirsave,
imrange,
TypeGrid='CartesMesh',
Nz=10, # tune this parrameter if you wish
Ny=1, # tune this parrameter if you wish
Nx=1, # tune this parrameter if you wish
verbose=1,
structured=False)
Path exist: True
CartesPorosity_001: done
CartesPorosity_002: done
CartesPorosity_003: done
CartesPorosity_004: done
CartesPorosity_005: done
CartesPorosity_006: done
CartesPorosity_007: done
CartesPorosity_008: done
CartesPorosity_009: done
CartesPorosity_010: done
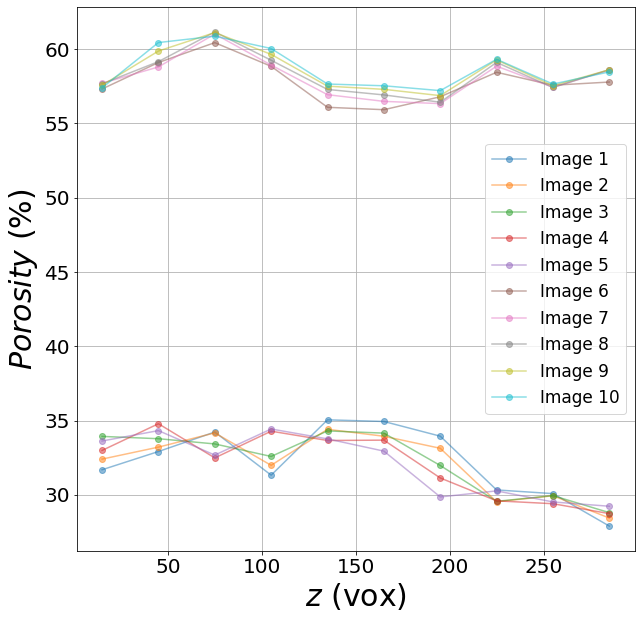
# We can plot the liquid fraction as a function of the z coordinate for the first image
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1, figsize = (10, 10))
for imi in imrange:
with open(dirsave+namesave+strindex(imi,3)+'.pkl','rb') as f:
pack = pkl.load(f)
lf = pack['lf']
z = pack['zgrid']
plt.plot(z, (1-np.asarray(lf))*100,'o-', alpha=0.5, label='Image {0}'.format(imi))
plt.xlabel(r'$z$ (vox)', fontsize=30)
plt.ylabel(r'$Porosity$ ($\%$)', fontsize=30)
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend(fontsize=17)
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x2b63b8aee2b0>
Porosity (in percent) as a function of the vertical position z (in voxels)
B) Individual pores properties
We are going to extract the individual pore volume, radius, sphericity, moment of inertial, strain tensor, etc.
These are the properties we are mainly interested in: - Volume \(V\) - Shape eigenvalues (\(S_1\),\(S_2\),\(S_3\)) - Elongation \(E\)
# Read/Save names and directories
nameread = 'PoreSeg_'
namesave = 'Props_'
dirread = ProcessPipeline[3]+'/'
dirsave = QuantFolders[1]+'/'
# Images indexes
imrange = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
Get some properties in the given field of view (field=[zmin,zmax,ymin,ymax,xmin,xmax])
Label and centroid coodinate: ‘lab’,‘z’,‘y’,‘x’
Volume, equivalent radius, area, sphericity: ‘vol’,‘rad’,‘area’,‘sph’
Volume from ellipsoid fit: ‘volfit’
Ellipsoid three semi-axis and eigenvectors: ‘S1’,‘S2’,‘S3’,‘e1z’,‘e1y’,‘e1x’,‘e2z’,‘e2y’,‘e2x’,‘e3z’,‘e3y’,‘e3x’,
Internal strain components: ‘U1’,‘U2’,‘U3’
Internal strain von Mises invariant: ‘U’
Oblate (-1) or prolate (1) ellipsoid:‘type’
# Region properties
RegionProp_Batch(nameread,
namesave,
dirread,
dirsave,
imrange,
verbose=True,
field=[40,220,40,220,40,220], # tune this parrameter if you wish
endread='.tif',
endsave='.tsv')
Path exist: True
Props_001: done
Props_002: done
Props_003: done
Props_004: done
Props_005: done
Props_006: done
Props_007: done
Props_008: done
Props_009: done
Props_010: done
# Read the regionprop files
properties_Beg = Read_RegionProp(namesave, dirsave, imrange[0:5])
# Read the regionprop files
properties_End = Read_RegionProp(namesave, dirsave, imrange[5:9])
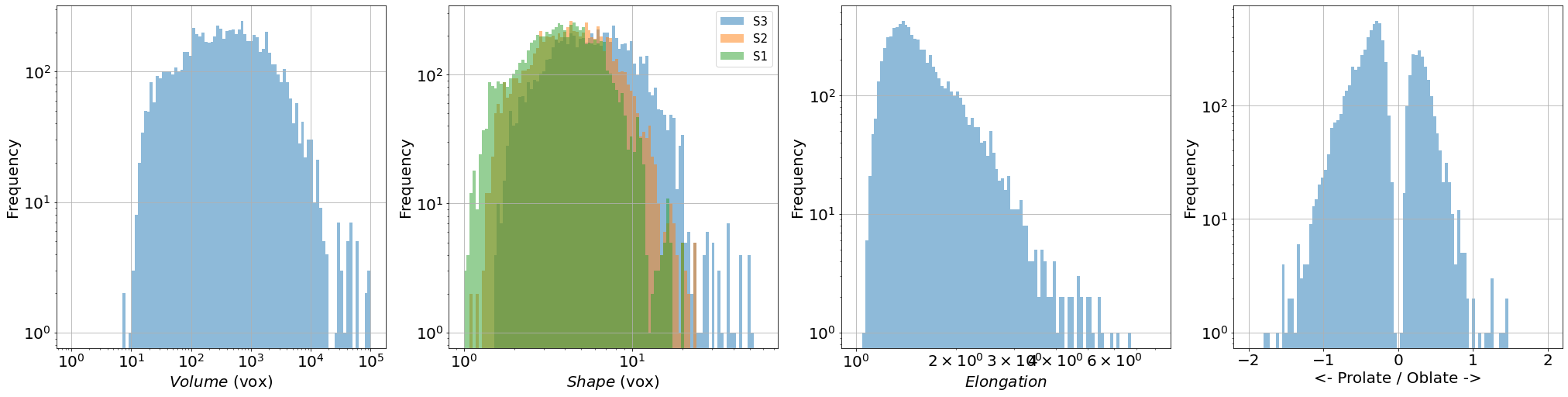
# histogram of some extracted properties
prop=['vol','S3','S2','S1','U','type']
xlab=[r'$Volume$ (vox)',r'$Shape$ (vox)',r'$Elongation$',r'<- Prolate / Oblate ->']
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,4, figsize = (7*4, 7), constrained_layout=True)
# Volume distribution of the pores
bins=np.power(10,np.linspace(np.log10(1),np.log10(1e5),100))
H=ax[0].hist(properties_Beg[prop[0]], bins=bins,alpha=0.5)
ax[0].set_xlabel(xlab[0], fontsize=20)
ax[0].set_ylabel(r'Frequency', fontsize=20)
ax[0].grid(True)
ax[0].set_yscale('log') # tune this parrameter if you wish
ax[0].set_xscale('log') # tune this parrameter if you wish
# Shape eigenvalues distribution of the pores
bins=np.power(10,np.linspace(np.log10(1),np.log10(60),100))
for i in range(3):
H=ax[1].hist(properties_Beg[prop[i+1]],
bins=bins,
alpha=0.5,
label=prop[i+1])
ax[1].set_xlabel(xlab[1], fontsize=20)
ax[1].set_ylabel(r'Frequency', fontsize=20)
ax[1].grid(True)
ax[1].set_yscale('log') # tune this parrameter if you wish
ax[1].set_xscale('log') # tune this parrameter if you wish
ax[1].legend(fontsize=15)
# Elongation distribution of the pores: shape eig max / eig min
bins=np.power(10,np.linspace(np.log10(1),np.log10(8),100))
H=ax[2].hist(properties_Beg[prop[1]] / properties_Beg[prop[3]],
bins=bins,
alpha=0.5)
ax[2].set_xlabel(xlab[2], fontsize=20)
ax[2].set_ylabel(r'Frequency', fontsize=20)
ax[2].grid(True)
ax[2].set_yscale('log') # tune this parrameter if you wish
ax[2].set_xscale('log') # tune this parrameter if you wish
# Deviation from a spherical shape: how oblate or prolate are the pore?
bins=np.linspace(-2,2,100)
H=ax[3].hist(properties_Beg[prop[4]] * properties_Beg[prop[5]],
bins=bins,
alpha=0.5)
ax[3].set_xlabel(xlab[3], fontsize=20)
ax[3].set_ylabel(r'Frequency', fontsize=20)
ax[3].grid(True)
ax[3].set_yscale('log') # tune this parrameter if you wish
Individual pore properties histograms
C) Coordination \(Z\)
# Read/Save image names and directories
namesave = 'Contact_'
dirsave = ProcessPipeline[6]+'/'
# Images indexes
imrange = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
# Read the first image of the series
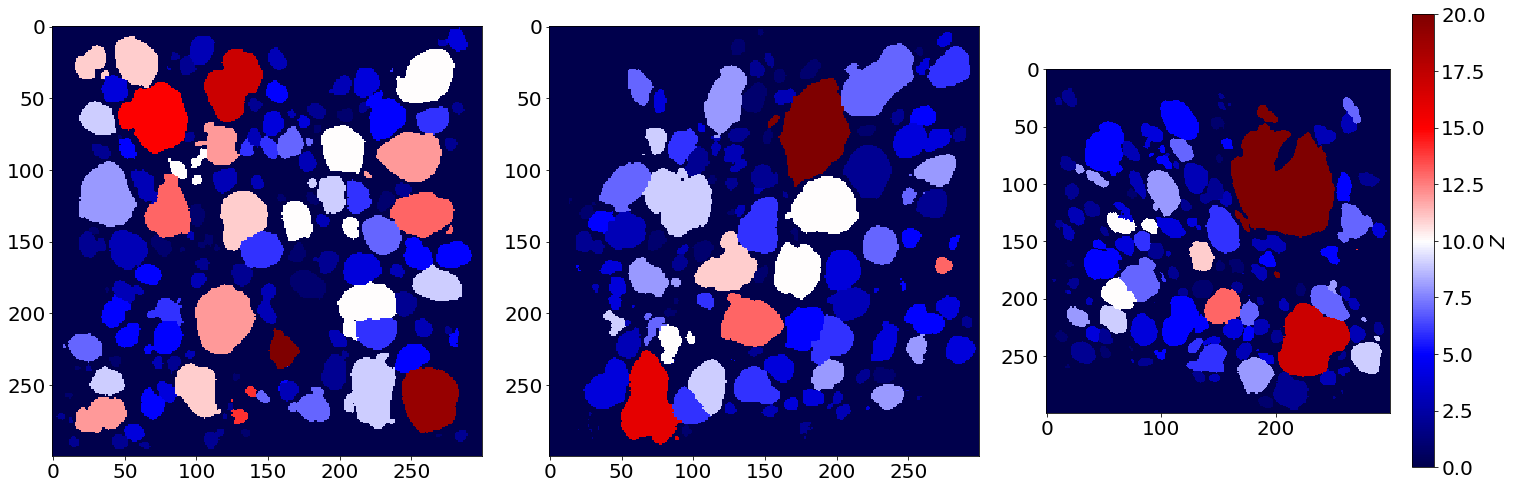
Lab = imread(dirsave+'Coordination_'+strindex(imrange[0], 3)+'.tif')
# Show a 3D-cut view of the volume
fig,ax,neg = Cut3D(Lab,
cmap='seismic',
interpolation='nearest',
figblocksize=7,
returnfig=True,
vmin=0,
vmax=20)
fig.colorbar(neg[2], label=r'$Z$')
# Read the last image of the series
Lab = imread(dirsave+'Coordination_'+strindex(imrange[-1], 3)+'.tif')
# Show a 3D-cut view of the volume
fig,ax,neg = Cut3D(Lab,
cmap='seismic',
interpolation='nearest',
figblocksize=7,
returnfig=True,
vmin=0,
vmax=20)
fig.colorbar(neg[2], label=r'$Z$')
vmin = 0 vmax = 20
/gpfs/offline1/staff/tomograms/users/flosch/Old/PSI_2021_Bread/FoamQuant/Figure.py:78: UserWarning: This figure was using constrained_layout==True, but that is incompatible with subplots_adjust and or tight_layout: setting constrained_layout==False.
plt.tight_layout()
vmin = 0 vmax = 20
<matplotlib.colorbar.Colorbar at 0x2b643aef7340>
Coordination image of the first image of the series (in the beginning of baking)
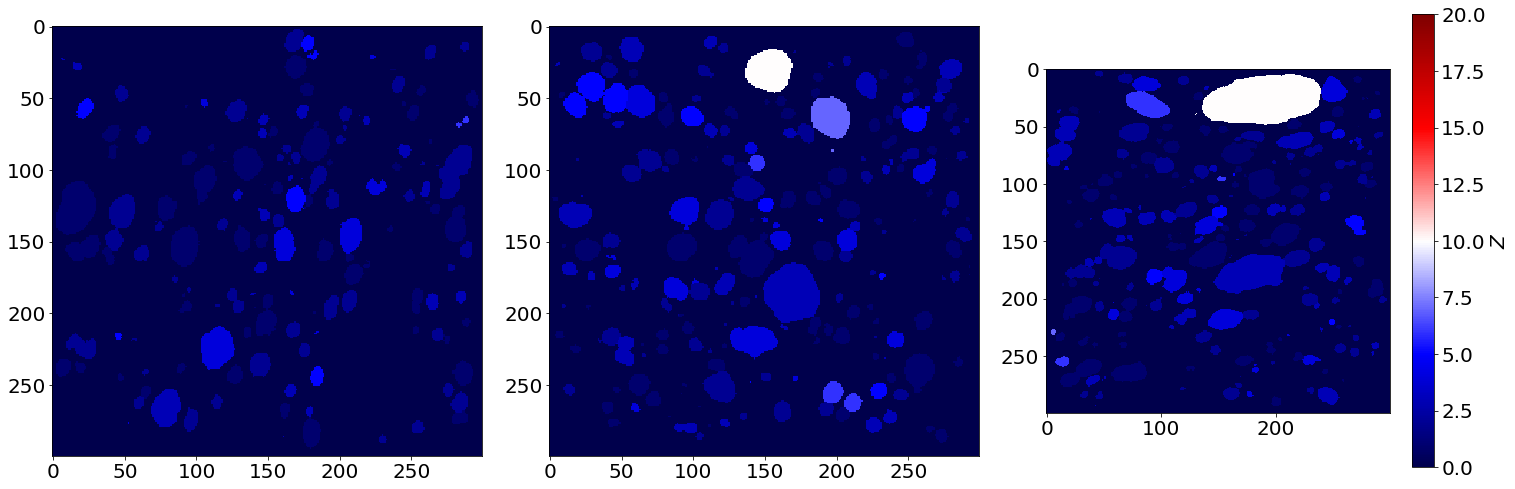
Coordination image of the last image of the series (in the end of baking)
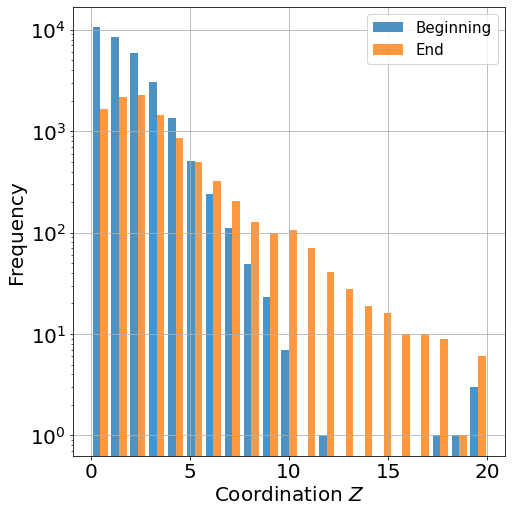
# Read contact table
TableFirst = ReadContactTable(namesave+'table_', dirsave, imrange[:5], verbose=False)
TableLast = ReadContactTable(namesave+'table_', dirsave, imrange[5:], verbose=False)
# remove the values at the edge
LZnoedge=[]
for Table in [TableFirst, TableLast]:
Znoedge = []; coordnoedge = []
for t in range(len(Table)):
table = Table[t]
for i in range(len(table['Z'])):
if table['lab_noedge'][i]>0:
Znoedge.append(table['Z'][i])
coordnoedge.append([table['z'][i],table['y'][i],table['x'][i]])
coordnoedge = np.asarray(coordnoedge)
LZnoedge.append(Znoedge)
# Coordination histogram before and after removing the edge pores
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1, figsize = (7, 7), constrained_layout=True)
H=ax.hist(LZnoedge, bins=21, label=['Beginning','End'], alpha=0.8)
ax.set_xlabel(r'Coordination $Z$', fontsize=20)
ax.set_ylabel(r'Frequency', fontsize=20)
ax.grid(True)
ax.set_yscale('log')
ax.legend(fontsize=15)
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x2b643afaccd0>
Coordination histogram
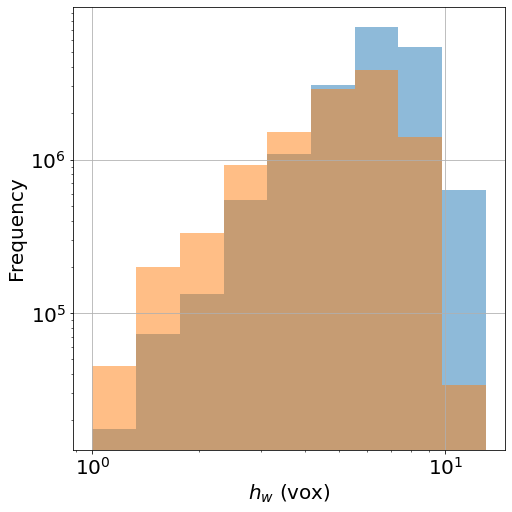
C) Local Wall Thickness \(h_w\)
def Remove0Array(image):
import numpy as np
ZZ,YY,XX = np.shape(image)
Array0 = np.reshape(image,(ZZ*YY*XX))
Array=[]
for i in range(len(Array0)):
if Array0[i]>0:
Array.append(Array0[i])
return Array
# Load first image as list
WTFirstList = Remove0Array(WTFirst)
WTFirstLast = Remove0Array(WTLast)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1, figsize = (7, 7), constrained_layout=True)
bins=np.power(10,np.linspace(np.log10(1),np.log10(13),10))
H=plt.hist(WTFirstList, alpha=0.5, bins=bins, label='beginning')
H=plt.hist(WTFirstLast, alpha=0.5, bins=bins, label='end')
ax.set_xlabel(r'$h_w$ (vox)', fontsize=20)
ax.set_ylabel(r'Frequency', fontsize=20)
ax.grid(True)
ax.set_yscale('log') # tune this parrameter if you wish
ax.set_xscale('log') # tune this parrameter if you wish
Local-wall thickness histogram
You have now completed the jupyter example for analysis on bread! We hope this has been useful to you!
For more information on the tools, the references or contacts, have a look on https://foamquant.readthedocs.io